- 25216 Nagway Road, Calgary, T3RIAl
- tle.clinic.calgary@gmail.com
- 825-474-4771
Type 2 Diabetes ccan be Reserved Through Physician Led Life Style Interventions.
Calgary Obesity Program
Obesity Management
The Lifestyle Clinic and Diabetes and Endocrinology Clinic of Alberta(DECA) has started a Medical Obesity Management Program to address the growing epidemic of obesity in Alberta. Calgary Obesity Program is a tailored multidisciplinary approach structured in a program to achieve sustainable weight reduction. It involves a comprehensive targeted approach that includes diet, exercise, behavior changes, and medical interventions.
Diabetes Management
Diabetes management entails maintaining healthy blood sugar levels through a combination of regular physical activity, a balanced diet, medication or insulin therapy as prescribed, monitoring blood glucose levels, and regular check-ups with healthcare professionals to prevent complications and promote overall well-being.
Endocrinology And General
Internal Medicine
Endocrinology is the branch of medicine that focuses on the endocrine system, which is responsible for producing and regulating hormones in the body. Endocrinologists diagnose and treat hormonal disorders, such as diabetes, thyroid disorders, and hormonal imbalances, through medication, lifestyle modifications, and other appropriate interventions.
Promoting Weight Loss, Diabetes Prevention through latest
medications, research and multidisciplinary approach , contact
for information
Program Component

Medical Management
Our obesity management program integrates diet, exercise, medication, and medical interventions. Guided by evidence-based practices, our experts use a long-term, multidisciplinary approach to help individuals achieve and maintain weight loss through personalized care plans, ongoing support, and sustainable strategies tailored to each person's unique health needs and goals.

Nutrition/Lifestyle Management
Lifestyle management for obesity emphasizes healthy habits, regular exercise, and a balanced, nutrient-rich diet. Identifying and correcting micronutrient deficiencies is crucial for overall health. Our experts provide personalized care to support sustainable weight loss, helping you achieve long-term results without compromising your nutritional needs or overall physical and mental well-being.

Mental Wellbeing
Addressing mental well-being is essential in obesity management, as it affects eating behavior, emotional health, and overall wellness. The Calgary Obesity Program supports your weight loss journey by providing mental health resources, counseling, and guidance, recognizing the strong connection between mental and physical health to help you achieve lasting, sustainable results.
Program Component
Medical Management
Diet, exercise, medication, and interventions for medical management of obesity. Our experts utilize latest evidence based management following a long term multidisciplinary approach combined with medication to achieve the desired results.
Nutrition/Lifestyle Management
Incorporating healthy habits, regular exercise, and a balanced diet are key components of lifestyle management for obesity prevention and treatment. While establishing a nutrient rich diet focused on weight reduction is important, it is paramount that body’s micronutrients are evaluated and any deficiency is addressed. Our experts will ensure you can achieve results without compromising your health.
Mental Wellbeing
Addressing mental wellbeing is important in obesity management, as it can impact eating behaviors, emotional health, and overall well-being. As part of this program we endeavour to support your weight loss journey with mental health support.
How to see our specialist?
1
GET A REFERRAL FROM YOUR Family Physicia / GP
To access our specialist care, it is essential to obtain a referral from your primary care physician.Referrals can be submitted to us via fax, mail, or by contacting our office directly.
2
OBTAIN A VIRTUAL CONSULTATION FROM ONE OF
OUR SPECIALIST
We provide virtual consultation across Alberta. Once we have received the referral form, we will promptly get in touch with you and provide you an appointment with one of our specialists. This appointment can be conducted In-Person or conveniently online, allowing you to participate from the comfort of your own home or via any mobile device.
3
OBTAIN IN PERSON/VIRTUAL CONSULTATIOON
WITH OUR SPECIALIST WITHOUT A REFERRAL
Want to see an endocrinologist without a referral? For problems related to diabetes, obesity, thyroid issues and PCOS you can see one of our specialist by paying out of pocket – appointment can be in-person or from your phone, tablet or computer.
4
CONTINUED SUPPORT
Each patient will have individual physician visits scheduled to meet their health goals. These visits will involve re-evaluating diabetees / weight-related medical conditions and adjusting treatment plans accordingly. If necessary, more frequent individual follow-ups may be conducted.

Harvard Diet Plan
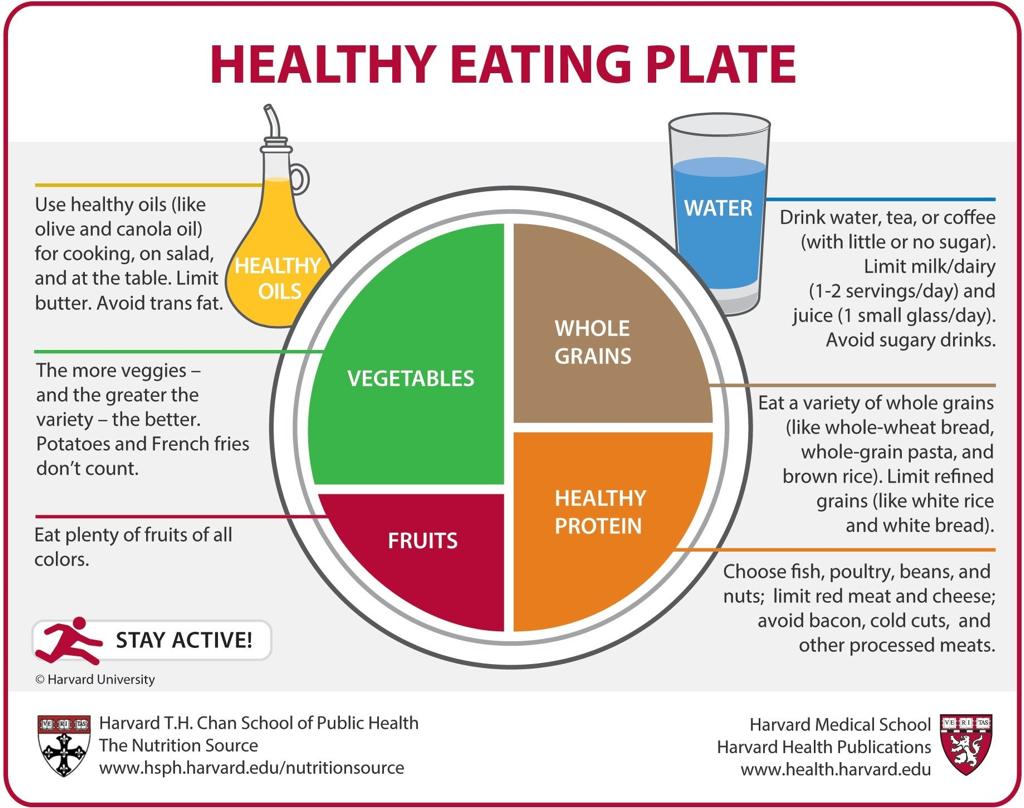
Harvard Diet Plan in English
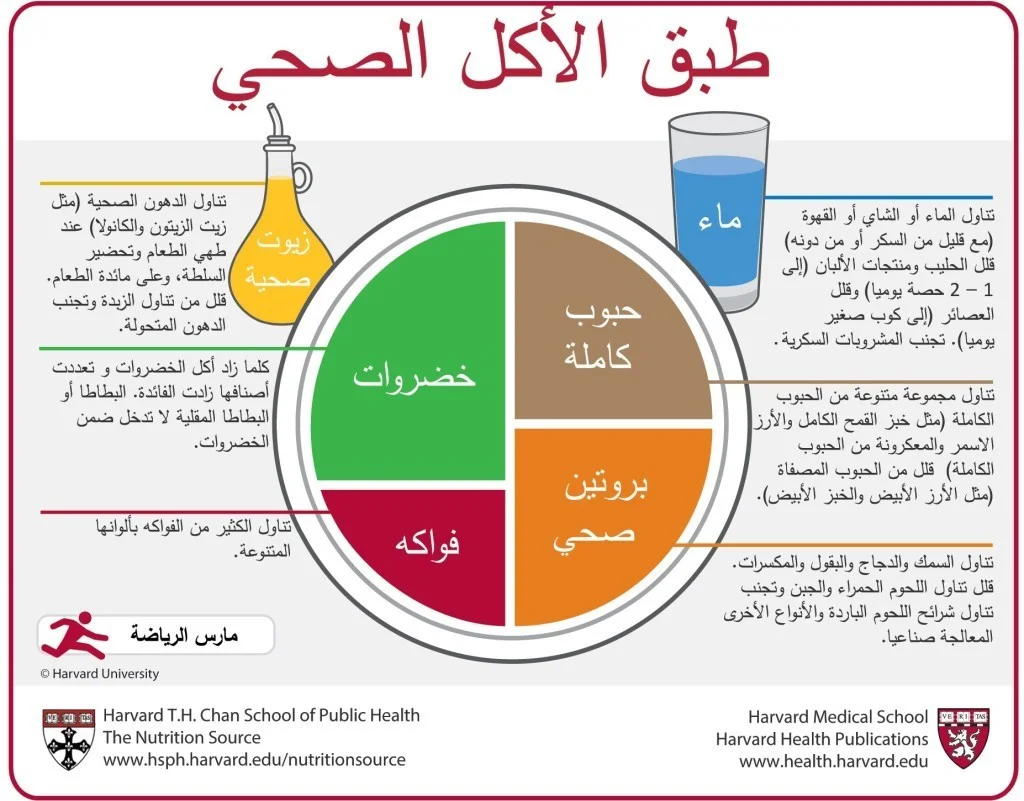
Harvard Diet Plan in Arabic
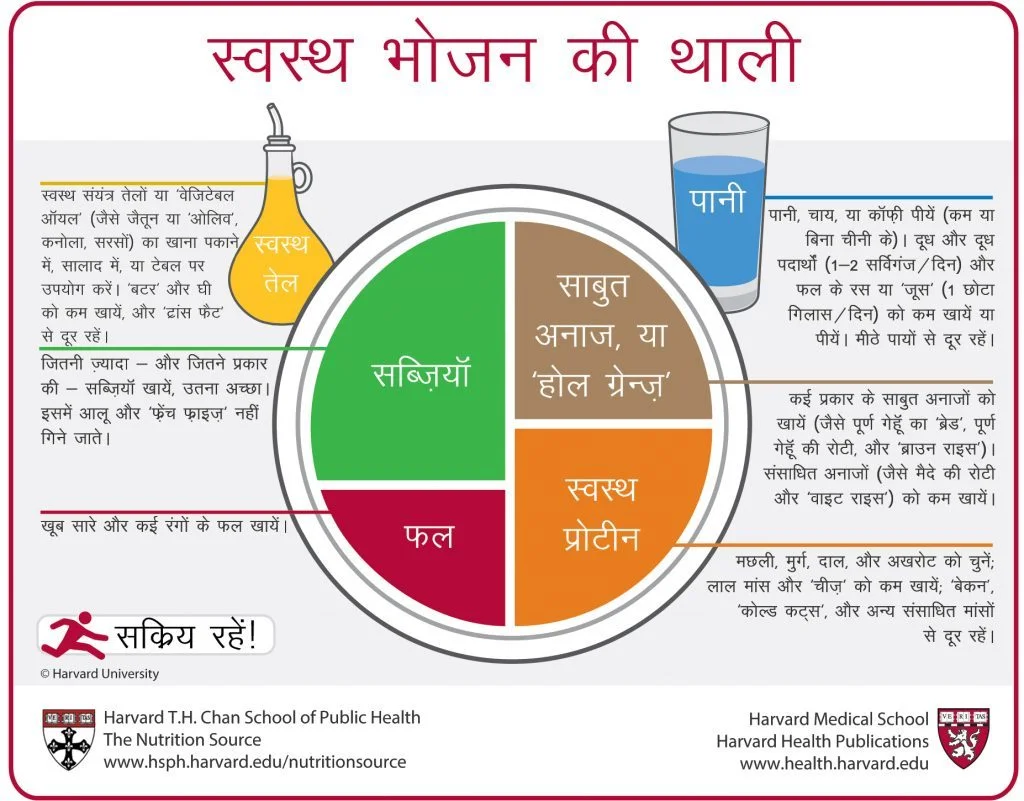
Harvard Diet Plan in Hindi
Our Specialist
Dr. Aashna Gill.
.B.B.S, F.R.C.P.C
Specialist in – General Internal Medicine
Diabetes, Endocrinology and Metabolism
FAQ
At present, we provide virtual consultation for long Distance Patient.
Diabetes cannot always be prevented, but there are steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes, which is the most common form of diabetes. Here are some recommendations:
1. Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity is a significant risk factor for type 2 diabetes. By achieving and maintaining a healthy weight, you can reduce your risk. Focus on a balanced diet that includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit your intake of sugary foods and beverages.
2. Exercise regularly: Engage in regular physical activity to help control your weight and improve insulin sensitivity. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, along with strength training exercises.
3. Make healthy food choices: Choose foods with a low glycemic index (GI), as they have a smaller impact on blood sugar levels. Include plenty of fiber-rich foods like whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables in your diet. Limit your intake of processed and sugary foods.
4. Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water and avoid sugary beverages like sodas and sweetened juices. Water is the best choice for staying hydrated without adding extra calories.
5. Limit alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. If you drink alcohol, do so in moderation.
6. Quit smoking: Smoking is not only a risk factor for various health conditions but also increases the risk of type 2 diabetes. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce your risk.
7. Get regular check-ups: Regular health check-ups can help monitor your blood sugar levels and detect any early signs of diabetes. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine the appropriate frequency of check-ups based on your individual risk factors.
It’s important to note that type 1 diabetes, which is an autoimmune condition, cannot be prevented. Additionally, there may be genetic factors or other underlying health conditions that can contribute to the development of diabetes. If you have a family history of diabetes or other risk factors, it’s essential to discuss preventive measures with your healthcare provider.
Diabetes cannot always be prevented, but there are steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes, which is the most common form of diabetes. Here are some recommendations: 1. Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity is a significant risk factor for type 2 diabetes. By achieving and maintaining a healthy weight, you can reduce your risk. Focus on a balanced diet that includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit your intake of sugary foods and beverages. 2. Exercise regularly: Engage in regular physical activity to help control your weight and improve insulin sensitivity. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, along with strength training exercises. 3. Make healthy food choices: Choose foods with a low glycemic index (GI), as they have a smaller impact on blood sugar levels. Include plenty of fiber-rich foods like whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables in your diet. Limit your intake of processed and sugary foods. 4. Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water and avoid sugary beverages like sodas and sweetened juices. Water is the best choice for staying hydrated without adding extra calories. 5. Limit alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. If you drink alcohol, do so in moderation. 6. Quit smoking: Smoking is not only a risk factor for various health conditions but also increases the risk of type 2 diabetes. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce your risk. 7. Get regular check-ups: Regular health check-ups can help monitor your blood sugar levels and detect any early signs of diabetes. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine the appropriate frequency of check-ups based on your individual risk factors. It’s important to note that type 1 diabetes, which is an autoimmune condition, cannot be prevented. Additionally, there may be genetic factors or other underlying health conditions that can contribute to the development of diabetes. If you have a family history of diabetes or other risk factors, it’s essential to discuss preventive measures with your healthcare provider.
Yes their are medications that help treat diabetes and promote weight loss for further information see one of our specialist.
Regular aerobic exercise is highly recommended to reduce the risk of diabetes and aid in weight loss. Aerobic exercises are activities that increase your heart rate and breathing for an extended period. They help improve insulin sensitivity, control blood sugar levels, and promote weight loss by burning calories. Some effective aerobic activities include:
1. Brisk walking: Walking at a faster pace than usual, ideally for 30 minutes or more, can be an excellent low-impact aerobic exercise.
2. Running/jogging: These high-impact activities can burn a significant number of calories and improve cardiovascular fitness. Start gradually if you are a beginner.
3. Cycling: Riding a bicycle is a great way to engage your leg muscles, boost your heart rate, and burn calories. It can be done outdoors or on a stationary bike indoors.
4. Swimming: Swimming is a low-impact exercise that works out your entire body. It is gentle on the joints and offers cardiovascular benefits.
5. Dancing: Engaging in dance forms like Zumba, aerobics, or even joining dance classes can provide an enjoyable way to improve fitness while burning calories.
6. High-intensity interval training (HIIT): HIIT involves short bursts of intense exercise alternated with brief recovery periods. It can be done with various activities like running, cycling, or bodyweight exercises.
7. Aerobic classes: Participating in classes like step aerobics, kickboxing, or cardio dance can make exercising more engaging and motivating.
Remember to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new exercise program, especially if you have pre-existing medical conditions or concerns. They can provide personalized recommendations based on your specific needs and fitness level.
A diet that can help prevent diabetes and promote weight loss is a balanced and healthy eating plan. One such diet that has been shown to be effective is the Mediterranean diet.
The Mediterranean diet is characterized by:
1. High consumption of fruits and vegetables: These provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber while being low in calories.
2. Whole grains: These include foods like whole wheat bread, brown rice, and whole grain pasta, which are rich in fiber and help regulate blood sugar levels.
3. Lean proteins: Sources of protein in the Mediterranean diet include fish, poultry, legumes, and nuts. These are healthier alternatives to red meat and processed meats, which have been linked to an increased risk of diabetes and weight gain.
4. Healthy fats: The Mediterranean diet emphasizes the consumption of healthy fats such as olive oil, avocados, and nuts. These fats are monounsaturated and polyunsaturated, which can help improve insulin sensitivity and promote heart health.
5. Limited sugar and processed foods: The Mediterranean diet discourages the consumption of sugary beverages, sweets, and processed foods, which are often high in added sugars and unhealthy fats.
The Mediterranean diet has been associated with a reduced risk of developing type 2 diabetes, as well as improvements in weight management and overall health. However, it’s important to remember that individual dietary needs may vary, and it’s always a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian before making significant changes to your diet.
Yes, certain hormone disorders can increase the risk of obesity and diabetes. Hormones play a crucial role in regulating various processes in the body, including metabolism, energy balance, and blood sugar control. When there is a hormonal imbalance, it can disrupt these processes and contribute to the development of obesity and diabetes.
Here are a few hormone disorders that can increase the risk of obesity and diabetes:
1. Insulin Resistance: Insulin resistance occurs when the body’s cells become less responsive to the effects of insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. When this happens, the pancreas produces more insulin to compensate, leading to high levels of insulin in the blood. Insulin resistance is strongly associated with obesity and is a key factor in the development of type 2 diabetes.
2. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): PCOS is a hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. It is characterized by high levels of androgens (male hormones) and insulin resistance. Many women with PCOS also experience weight gain or obesity, and they have an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
3. Cushing’s Syndrome: Cushing’s syndrome is a condition characterized by the excessive production of cortisol, a hormone that helps regulate metabolism. High levels of cortisol can lead to weight gain, particularly in the abdominal area (central obesity). It can also cause insulin resistance and increase the risk of developing diabetes.
4. Hypothyroidism: Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones. Thyroid hormones play a crucial role in regulating metabolism. When levels of these hormones are low, it can lead to weight gain or difficulty losing weight. Obesity and hypothyroidism are often seen together, and hypothyroidism can also contribute to insulin resistance and an increased risk of diabetes.
It’s important to note that while hormone disorders can increase the risk of obesity and diabetes, they are not the sole causes of these conditions. Other factors such as genetics, lifestyle choices, and environmental factors also play significant roles. If you suspect you have a hormone disorder or are concerned about your risk of obesity or diabetes, it’s best to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation and personalized advice.